RC Receiver & Transmitter | Wireless Controller for RC Cars
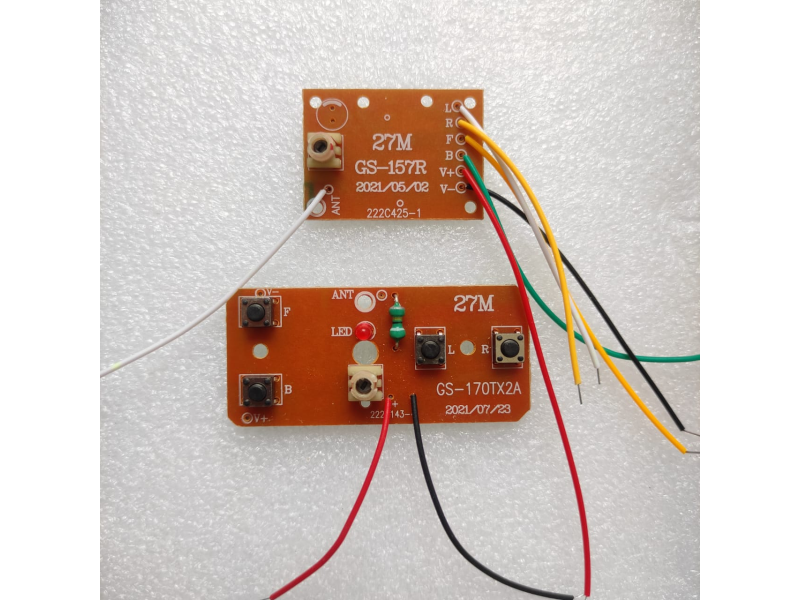
RC Receiver & Transmitter | Wireless Controller for RC Cars
Availability: In stock
Brand: Generic
SKU: RM018111
Product Highlights:
- Number of Channels : 4
- Frequency : 2.4GHz or 5.8GHz
- Modulation : FM (Frequency Modulation)
- Antenna, Transmitter & Receiver
A radio control (RC) receiver and transmitter are integral components of a remote control system used to operate RC vehicles, aircraft, boats, and other remote-controlled devices. The transmitter, often referred to as the radio controller or remote control, is held and operated by the user, while the receiver is installed in the RC vehicle or device.
Transmitter:
The transmitter is the handheld device that allows the user to control the RC vehicle or device. It typically consists of the following components:
1. Antenna: The antenna sends out the radio signals generated by the transmitter.
2. Controls: The transmitter features various controls such as joysticks, switches, buttons, or dials. These controls are used by the user to send commands to the RC vehicle or device, such as controlling its speed, direction, or other functions.
3. Power source: The transmitter is powered by batteries or rechargeable batteries, providing the necessary electrical energy to operate the device.
4. RF Module: The RF (Radio Frequency) module is responsible for generating and transmitting the radio signals from the transmitter to the receiver. It converts the user’s commands into radio signals that are then transmitted wirelessly to the receiver.
Receiver:
The receiver is installed in the RC vehicle or device and receives the radio signals sent by the transmitter. It typically consists of the following components:
1. Antenna: The receiver has an antenna that receives the radio signals sent by the transmitter.
2. RF Module: Similar to the transmitter, the receiver has an RF module that receives the radio signals and converts them into electrical signals.
3. Control outputs: The receiver is connected to the various control inputs of the RC vehicle or device, such as the motor speed controller, servo controllers, or other control mechanisms. It translates the received signals into commands that control the vehicle’s movement or specific functions.
4. Power source: The receiver requires power to operate and is usually connected to the vehicle’s power system or has its own battery or power source.
5. Signal processing circuitry: The receiver may also have circuitry to process and filter the received signals, ensuring reliable communication between the transmitter and receiver.
6. Binding/Pairing functionality: Many receivers feature binding or pairing functionality to establish a secure connection with a specific transmitter. This ensures that multiple RC systems can operate in the same area without interfering with each other.
The transmitter and receiver work together to establish a wireless communication link, allowing the user to control the RC vehicle or device remotely. The user’s commands are transmitted from the transmitter to the receiver via radio signals, which are then interpreted by the receiver to control the various functions of the RC vehicle or device.
Transmitter Specifications:
1. Number of Channels: RC transmitters can have different numbers of channels, typically ranging from 2 to 8 or more. Each channel allows control over a specific function or servo on the RC vehicle or device.
2. Frequency: The frequency refers to the radio frequency at which the transmitter operates. Common frequencies include 2.4GHz and 5.8GHz, which are widely used due to their reliability and reduced interference compared to older frequencies like 27MHz or 72MHz.
3. Modulation: Transmitters often use various modulation techniques to encode the control signals. Frequency Modulation (FM) and Amplitude Modulation (AM) are common modulation types.
4. Power Output: The power output of the transmitter determines the range and signal strength. It is usually measured in milliwatts (mW) or decibels (dBm). Higher power outputs generally offer longer control ranges.
5. Telemetry: Advanced transmitters may feature telemetry capabilities, allowing you to receive real-time data and information from the RC vehicle, such as battery voltage, speed, temperature, or GPS data.
6. Programming and Mixing: Some transmitters provide advanced programming features that allow you to customize and fine-tune control settings and servo mixing configurations to suit your specific needs.
Receiver Specifications:
1. Number of Channels: Receivers have a corresponding number of channels to match the transmitter. Make sure the receiver has an adequate number of channels to control all the necessary functions of your RC vehicle or device.
2. Compatibility: Ensure that the receiver is compatible with the frequency and modulation used by your transmitter. They need to match to establish a proper connection.
3. Fail-Safe: Many receivers offer fail-safe functionality, which means they can be programmed to automatically activate pre-determined servo positions in case of signal loss or interference. This helps prevent accidents or damage if the connection is lost.
4. Range: The range of the receiver refers to the maximum distance at which it can maintain a reliable connection with the transmitter. Range can vary depending on factors such as transmitter power output and environmental conditions.
5. Size and Weight: Consider the size and weight of the receiver, especially if you have space constraints or weight limitations in your RC vehicle or device.
It’s important to note that specific RC systems may have additional features, such as programmable mixes, adjustable settings, or compatibility with specific brands or models. Therefore, it’s always recommended to consult the product specifications provided by the manufacturer for detailed and accurate information on a particular RC receiver and transmitter system.

